Using AtScale Models in Power BI Composite Models
You can configure your AtScale models to be used in Microsoft Power BI composite models. This enables analysts to combine their organization's models with their own datasets to attain new insights, without relying on an external data team.
At a high level, configuring your AtScale models to be used in Power BI composite models involves the following steps:
- Configure AtScale to use the Tabular 1600 DAX dialect.
- Connect to your models from Power BI using AtScale's model-specific connection strings.
- Convert Power BI's live connection to your model to DirectQuery.
- Connect to your non-AtScale datasource from Power BI.
- Create the cross-datasource relationships from your AtScale model to your non-AtScale dataset.
These steps are described in the following sections.
For a demo of configuring composite model support in AtScale, see Power BI Composite Model Support on the AtScale Help Center.
Configure AtScale to use the Tabular 1600 DAX dialect
To enable composite model support, you must first configure AtScale to use the Tabular 1600 DAX dialect. To do this, set the xmla.discover.properties.daxdialect global setting to tabular1600.
For more information, see XMLA Settings and Configuring Global Settings.
Update your model connection string
Next, you need to update your model connections in Power BI with the model-specific strings generated by AtScale:
-
Deploy your catalog, if you haven't already.
-
Open the Deployed Catalogs panel and select your catalog.
-
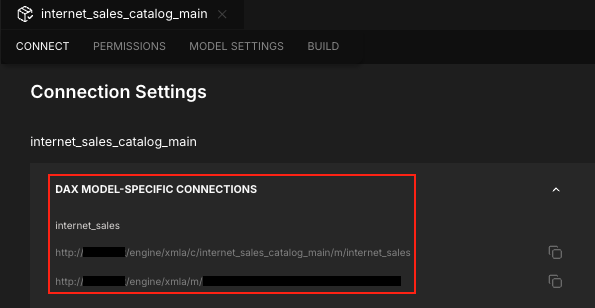
On the Connect tab, expand the DAX Model-Specific Connections section.
-
Copy the connection string for the model you want to connect to. Each model has two strings:
- One with the human-readable format
http://<host>/engine/xmla/c/<catalog>/m/<model>. - One with the shortened, token-based format
http://<host>/engine/xmla/m/<token>.
You can use either string to connect to the model. However, because Power BI imposes a character limit on server names, you may need to use the token-based string if your catalog or model names are too long.
- One with the human-readable format
-
Use the connection string to connect to your model from Power BI. Be sure to set the connection in the following places:
- Each Power BI workbook you want to use composite models in.
- Each Power BI Service datasource configuration for which you want to enable composite models.
Convert the model connection to DirectQuery
Next, you must convert Power BI's connection to the model from a live connection to DirectQuery. For more information on DirectQuery, refer to the Power BI documentation.
- In Power BI, click the Modeling tab, then click Make changes to this model.
- In the A DirectQuery connection is required dialog, click Add a local model.
- In the Connect to your data dialog, select your model, then click Submit.
Connect to your non-AtScale datasource
Next, you must connect to your non-AtScale datasource from Power BI. For instructions, refer to the Microsoft Power BI documentation.
AtScale has verified Power BI's client-side composite modeling behavior with client-side .xls datasources. It is possible that certain datasource combinations are restricted in some way in Power BI. If you encounter problems with a particular combination that you believe to be caused by AtScale, contact AtScale Support.
Create the cross-datasource relationships
Finally, you need to create relationships from your AtScale model to your non-AtScale dataset.
When creating these relationships, consider the following:
-
Think of the non-AtScale datasource as a fact table with dimension keys.
- Think of dimension keys as representing a degenerate dimension that has key values that match the corresponding AtScale dimension key values.
- Create relationships dimension-to-dimension (i.e., on conformed dimensions).
-
The data types for both key values used should be the same. In particular, pay attention to datetime columns.
-
The AtScale side of the relationship must be a dimensional attribute. It cannot be a database column.
- The relationship is made to the AtScale "Value" attribute.
- AtScale dedupes dimensional members by key. If you've followed best-practices and made your "Value" values unique, then AtScale will always be on a "1" side of the relationship.
-
Interpretation of Power BI's cardinality type (for example, (1:*)) is always relative to the "from" side of the relationship, which depends on the drag-drop order.
The following relationship types are supported:
- One to many (1:*)
- One to one (1:1)
- Many to many (*:*)
- Many to one (*:1) (see note)
Many-to-one relationships are not supported when AtScale is on the "many" side. If your model falls into this category, then the AtScale attribute's "value" column mapping should be reconsidered.
Once you have created the relationships between your AtScale model and non-AtScale dataset, you can use your composite model in reports.
Performance notes
Filtered DirectQuery queries are sent to AtScale, but Power BI's query engine performs client-side processing to combine the two datasets. As a result, the machine that is running Power BI (either Desktop or Cloud) must have enough memory to handle the data processing job you are trying to accomplish. Use plenty of filters to try to keep extraction sizes small. AtScale does not recommend trying to analyze billions of records this way.