Use cases for Time Dimensions
The following use cases are examples from AtScale's Sales Insights demo data, in which time dimensions are used for time-based sales analysis. The calculated measures shown in each MDX example use the following time intelligence MDX functions to navigate through time dimensions: LEAD, LAG, PREVMEMBER, NEXTMEMBER, CURRENTMEMBER, PERIODSTODATE, and PARALLELPERIOD.
- Period-over-period growth for sales amounts
- Sales growth year-over-year
- Sales year-to-date
- Sales year-to-date by day, compared to previous year
- Daily sales compared to 30-period moving average and standard deviation
- 30-period moving average compared to the previous year's
- 30-period moving average percent change compared to the previous year's
- 365-day moving window at levels higher than Day
- Subsets of children periods
Period-over-period growth for sales amounts
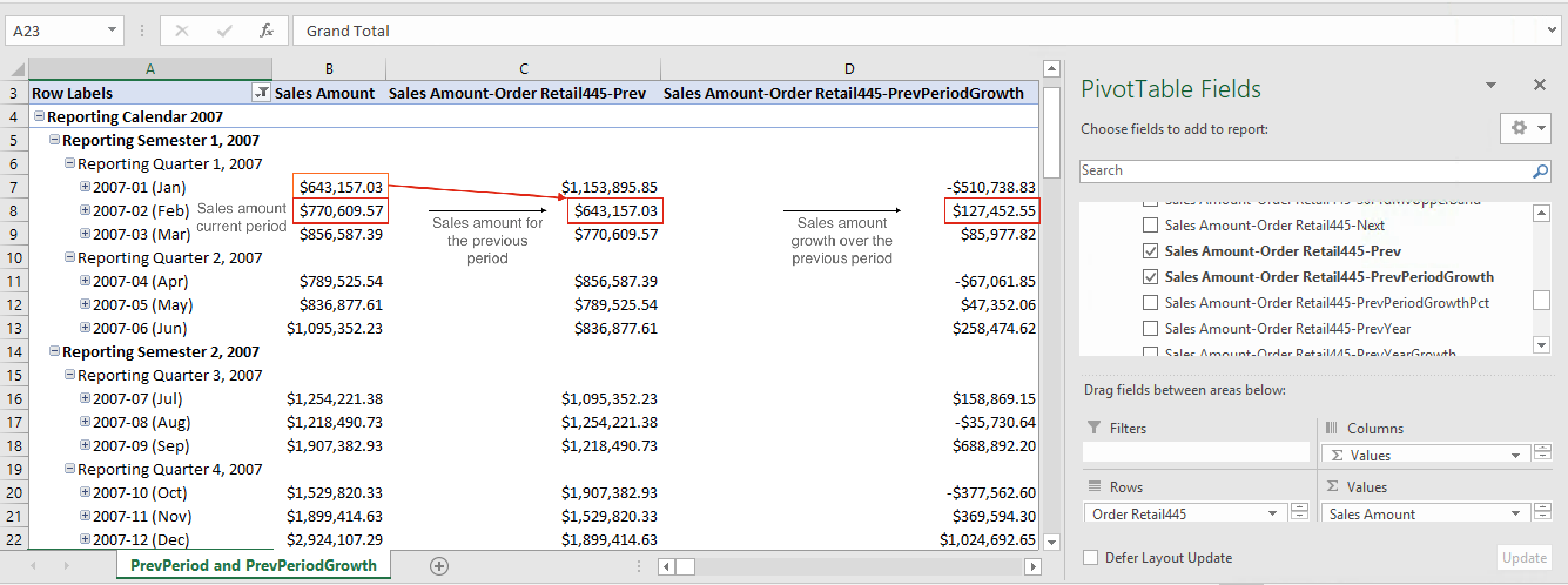
In this use case, the calculated measures below can be used to compare sales growth of the current period to the previous period. These calculated measures use CURRENTMEMBER, LAG, and PREVMEMBER to calculate the sales amount for the previous period and the sales amount growth over the previous period.
Case 1
Calculated measure for sales amount for the previous period:
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-Prev]
([Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember.PrevMember, [Measures].[salesamount1])
Case 2
Calculated measure for sales amount growth over the previous period:
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-PrevPeriodGrowth]
([Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember, [Measures].[salesamount1])
-
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-PrevYear]
Workbooks
Figure 1. Tableau workbook use cases 1 and 2
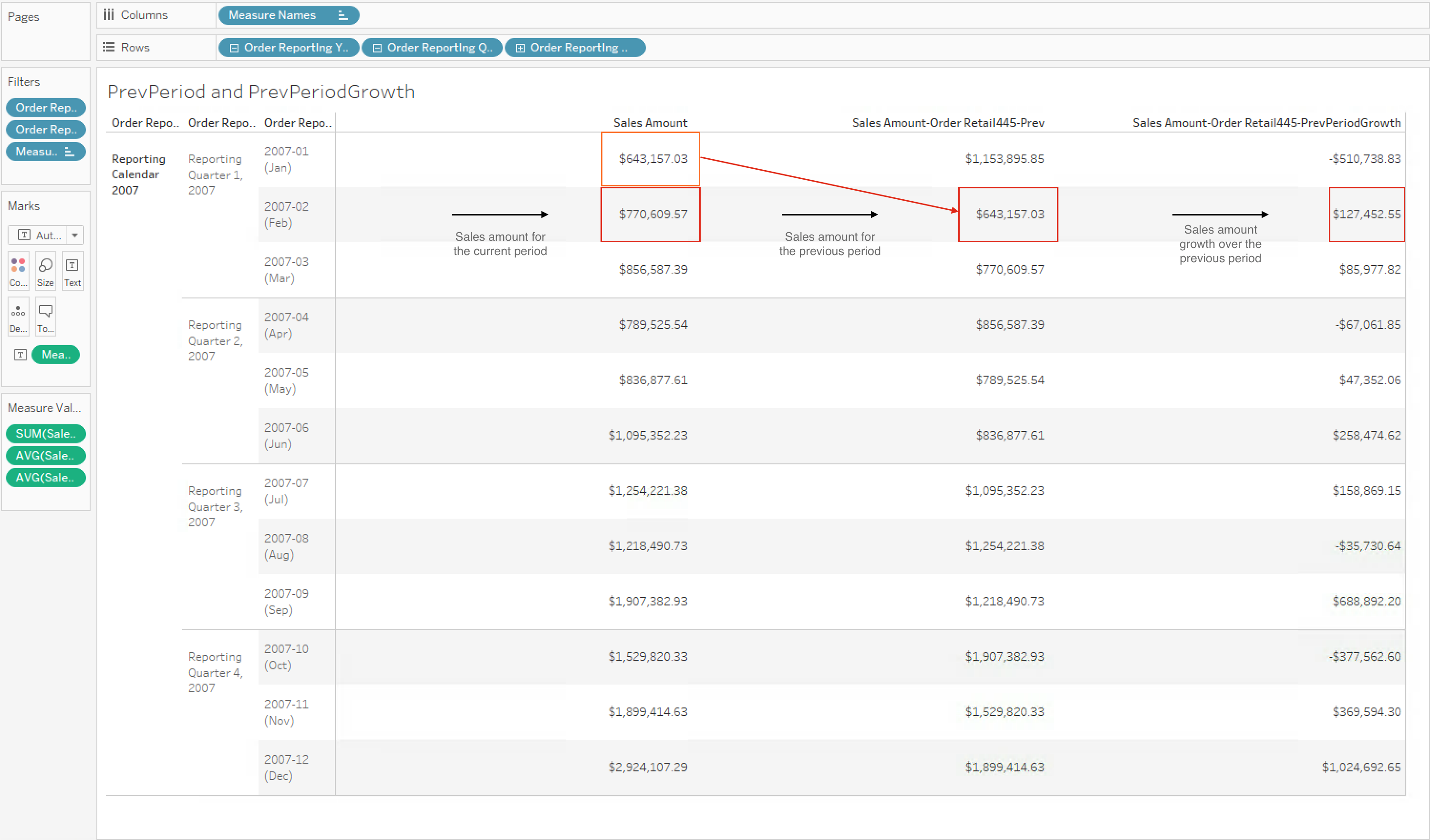
Figure 2. Excel workbook for use cases 1 and 2
Sales growth year-over-year
In this use case, the calculated measures below can be used to find the internet sales growth over one year (between now and the same time last year). The MDX expressions below use CURRENTMEMBER and PARALLELPERIOD.
Case 3
Calculated measure for internet sales from last year:
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-PrevYear]
(ParallelPeriod(
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].[Order Reporting_Year],
1,
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember),
[Measures].[salesamount1]
)
Case 4
Calculated measure for growth of internet sales between last year and
the current year:
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-PrevYearGrowth]
([Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember, [Measures].[salesamount1])
-
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-PrevYear]
Workbooks
Figure 3. Tableau workbook for use cases 3 and 4
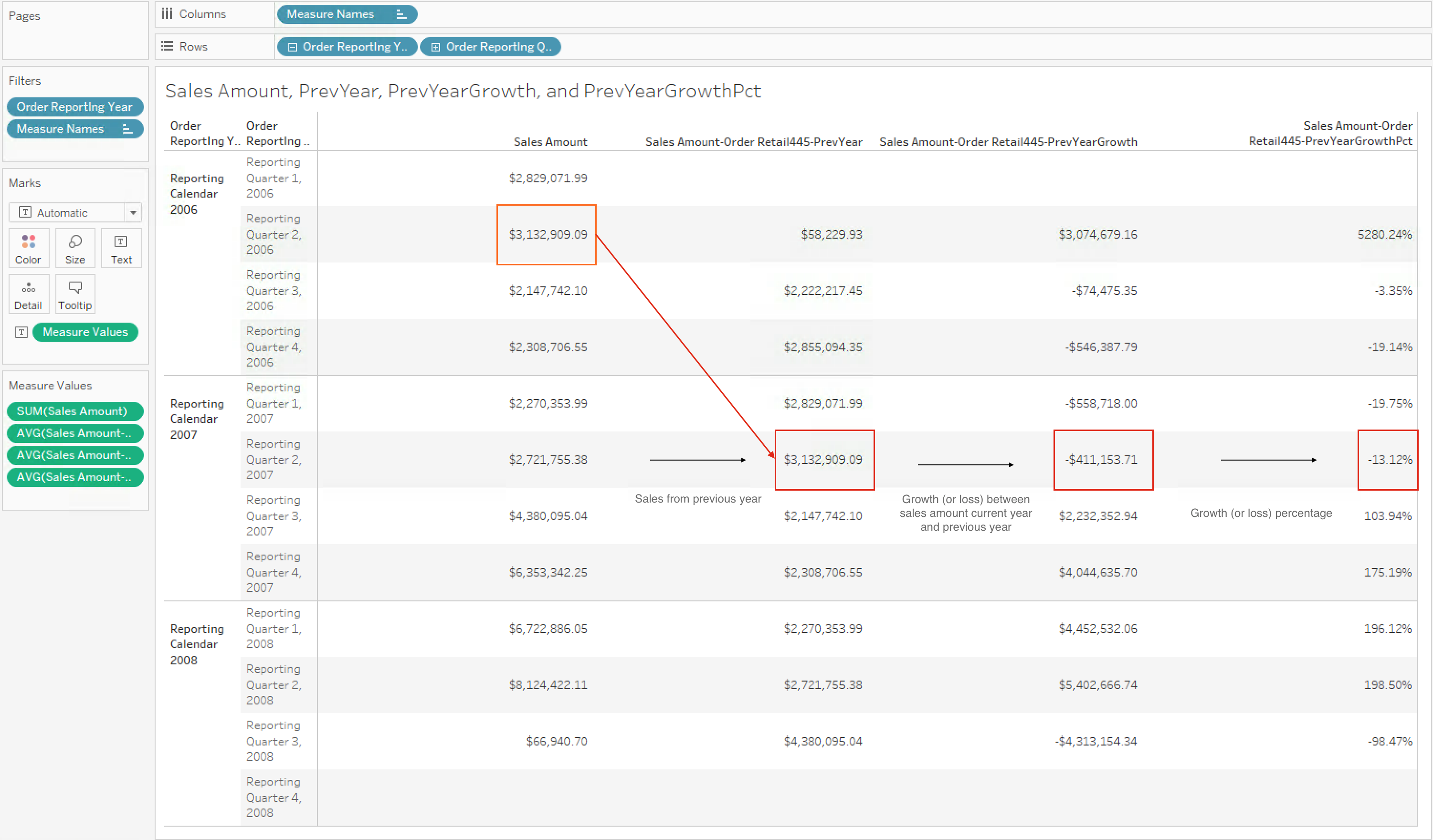
Figure 4. Excel workbook for use cases 3 and 4
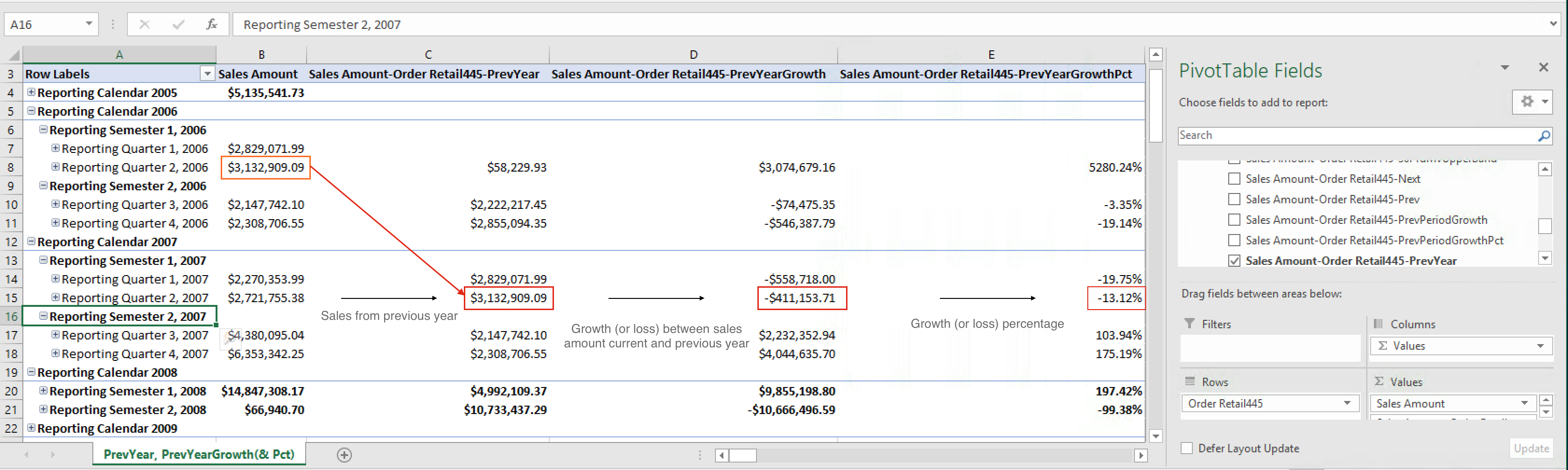
Sales year-to-date
In this use case, the calculated measure below can be used to find the internet sales for the year, ending with the current date.
Case 5
Calculated measure for the aggregate of sales for the year:
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-YTD]
MDX expression:
Aggregate(
PeriodsToDate(
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].[Order Reporting_Year],
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember
),
[Measures].[salesamount1]
)
Sales year-to-date by day, compared to previous year
In this use case, the calculated measure below can be used to compare the daily sales amount for the year-to-date, and the year-to-date sales of the year previous.
Case 6
Calculated measure for all internet sales of the year previous to the
current year: [Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-YTDPrevYear]
MDX expression:
Aggregate(
PeriodsToDate(
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].[Order Reporting_Year],
ParallelPeriod(
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].[Order Reporting_Year],
1,
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember
)
),
[Measures].[salesamount1]
)
Workbooks
Figure 5. Tableau workbook for use cases 5 and 6
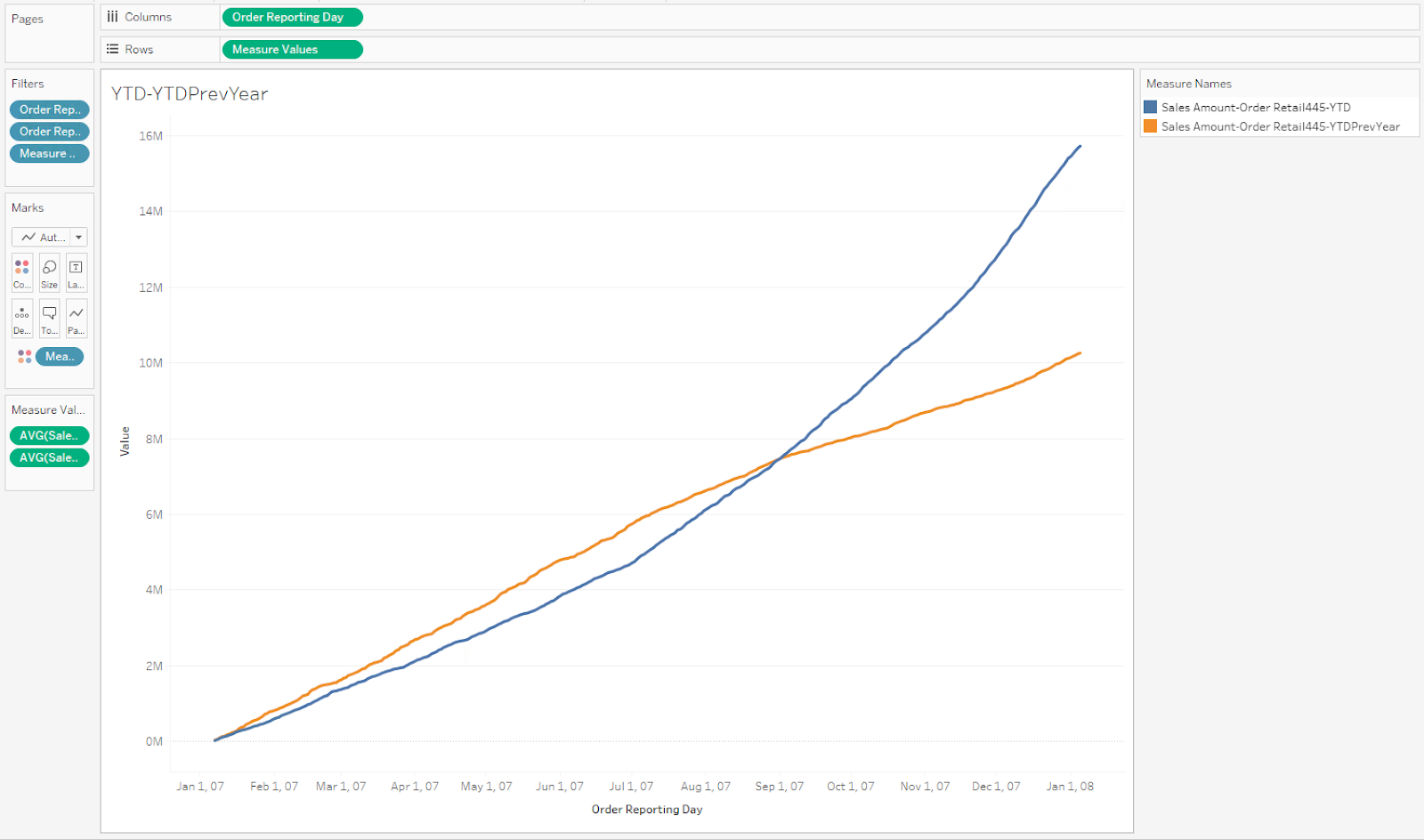
Figure 6. Excel workbook for use cases 5 and 6
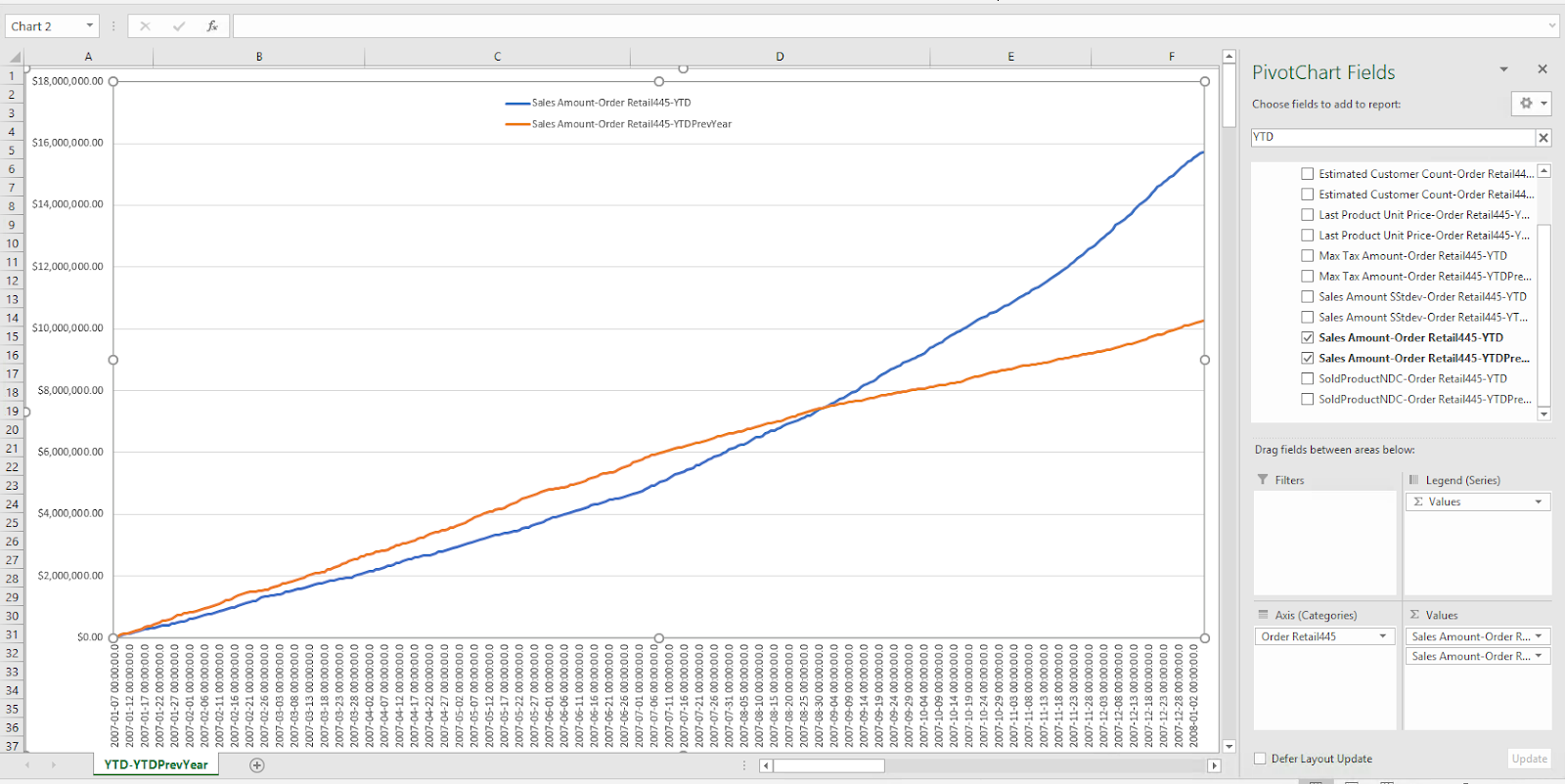
Daily sales compared to 30-period moving average and standard deviation
In this use case, the calculated measures can be used to compare each day's sales for the past 30 days, as well as each day's moving average of the previous 30 days. We can also find the upper and lower bounds of the daily moving average's standard deviation.
Case 7
Calculated measure for the 30-period moving average:
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvAvg] (Not that the
Range operator ":" is inclusive at both ends of the range, so use a lag
value of 29 to get a 30 period range.)
Avg(
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember.Lag(29)
:
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember,
[Measures].[salesamount1]
)
Case 8
Calculated measure for the 30-period moving average's standard
deviation: [Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvStdev]
Stdev(
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember.Lag(29)
:
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember,
[Measures].[salesamount1]
)
Case 9
Calculated measure for the standard deviation's upper bound:
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvUpperBand]
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvAvg]
+
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvStdev]
Case 10
Calculated measure for the standard deviation's lower bound:
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvLowerBand]
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvAvg]
-
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvStdev]
Workbooks
Figure 7. Tableau workbook for use cases 7, 8, 9 and 10
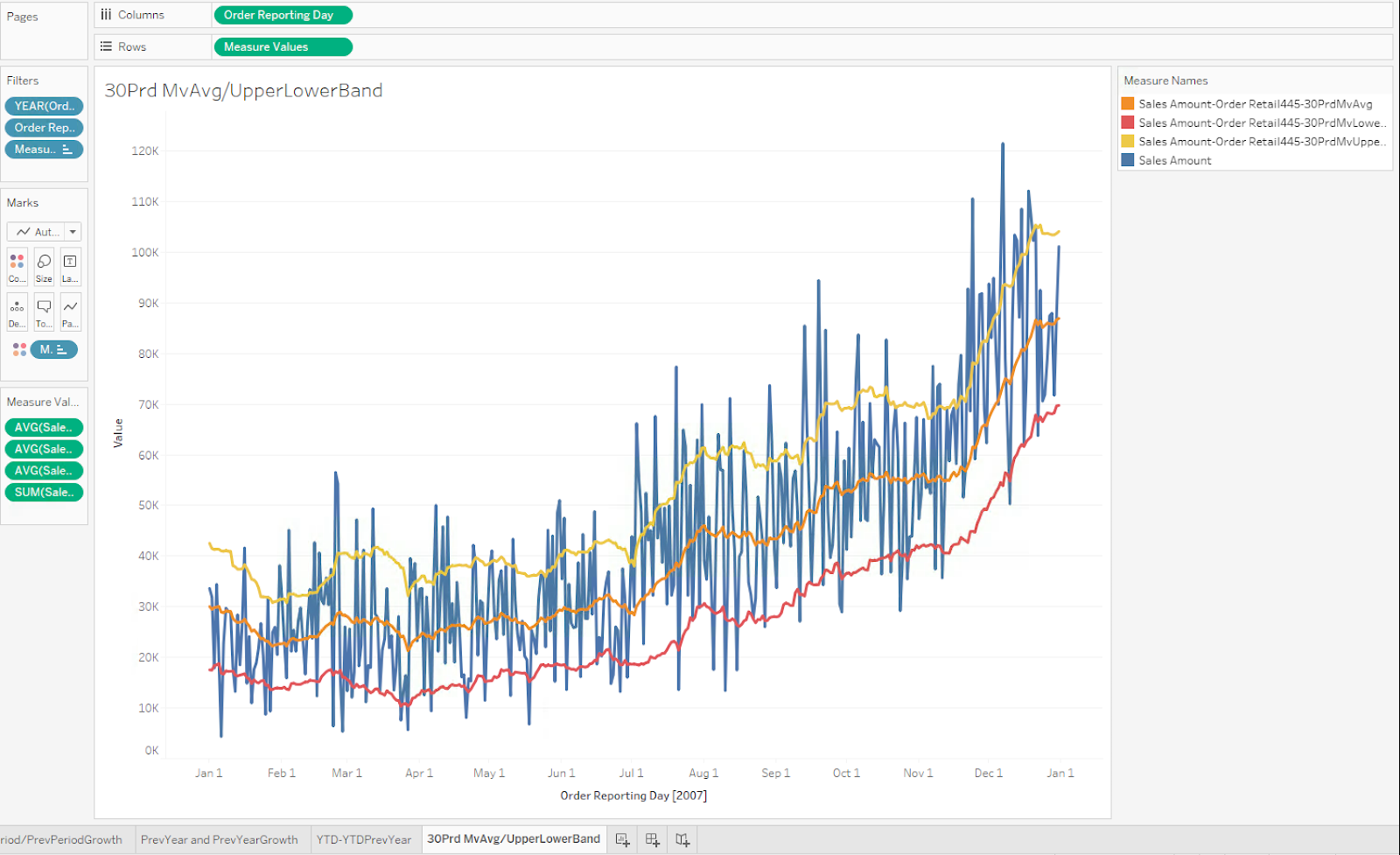
Figure 8. Excel visual representation for use cases 7, 8, 9 and 10
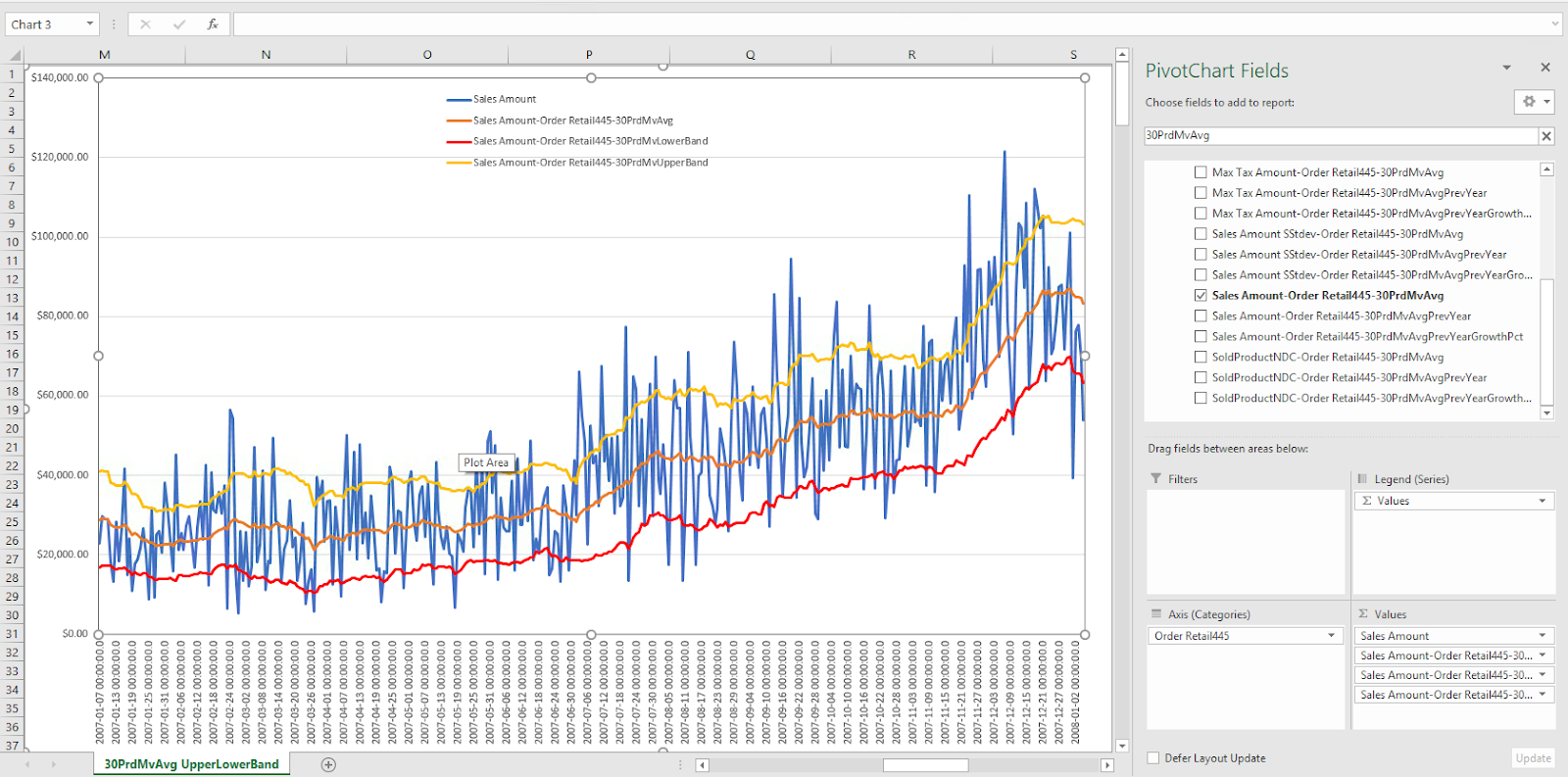
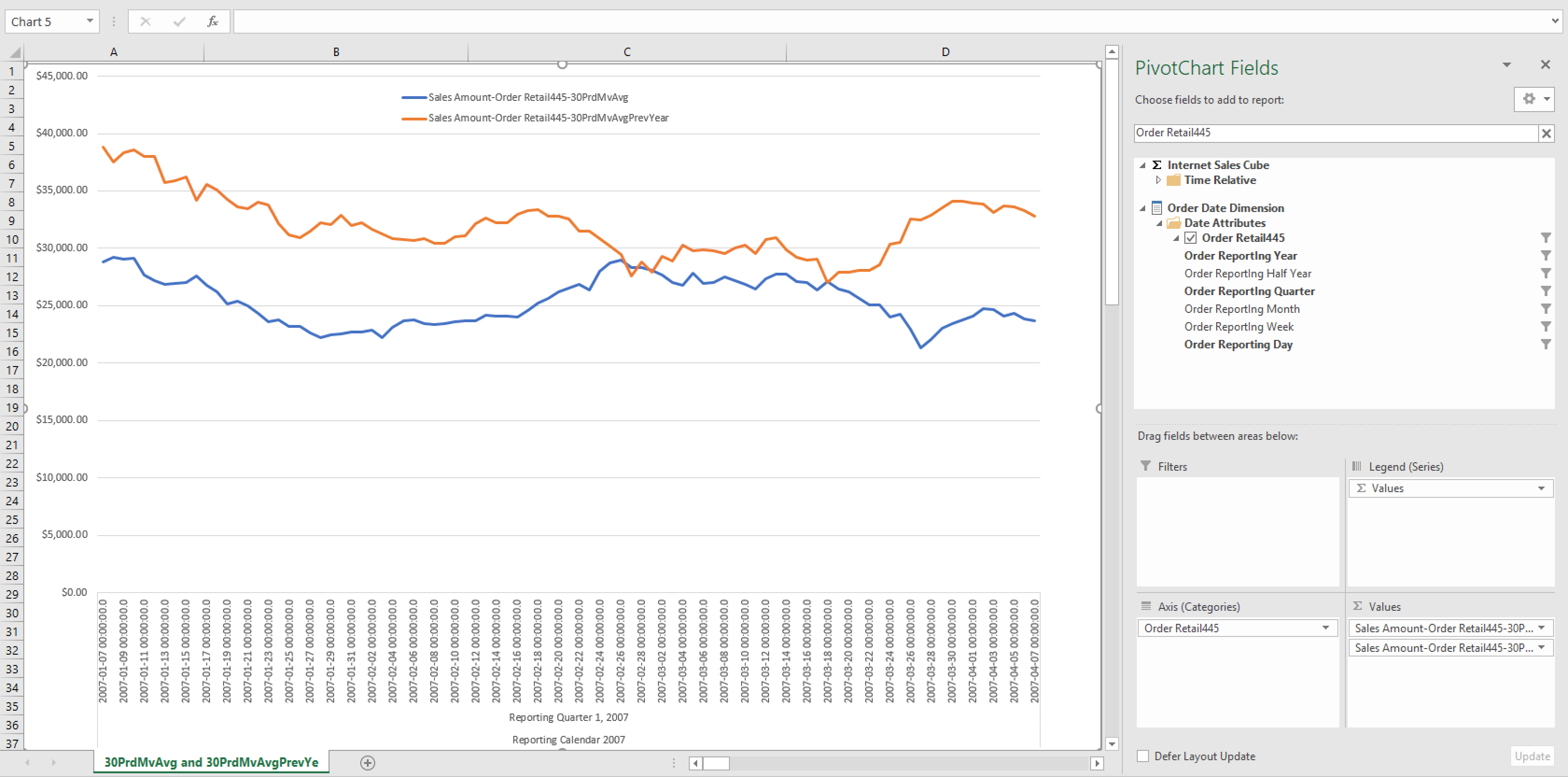
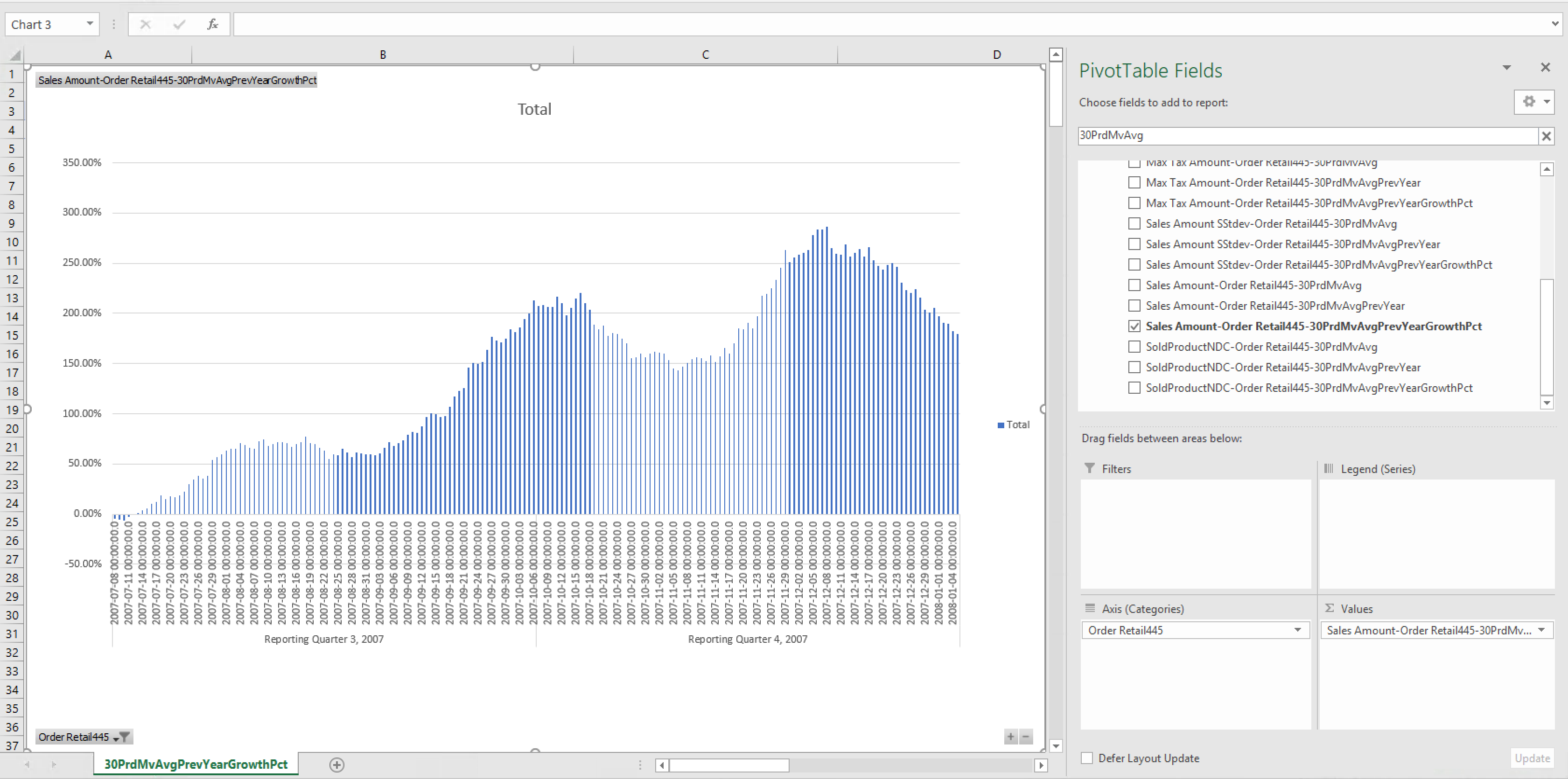
30-period moving average compared to the previous year's
This use case compares the moving average of sales for last 30 days, compared to the same period in the previous year.
Case 11
Calculated measure for the 30-period moving average in the previous
year: [Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvAvgPrevYear]
Avg(
ParallelPeriod(
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].[Order ReportIng_Year],
1,
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember
).Lag(29):
ParallelPeriod(
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].[Order ReportIng_Year],
1,
[Order Date Dimension].[Order Retail445].CurrentMember
),
[Measures].[salesamount1]
)
Workbooks
Figure 9. Tableau workbook for use case 11 against 30PrdMvAvg
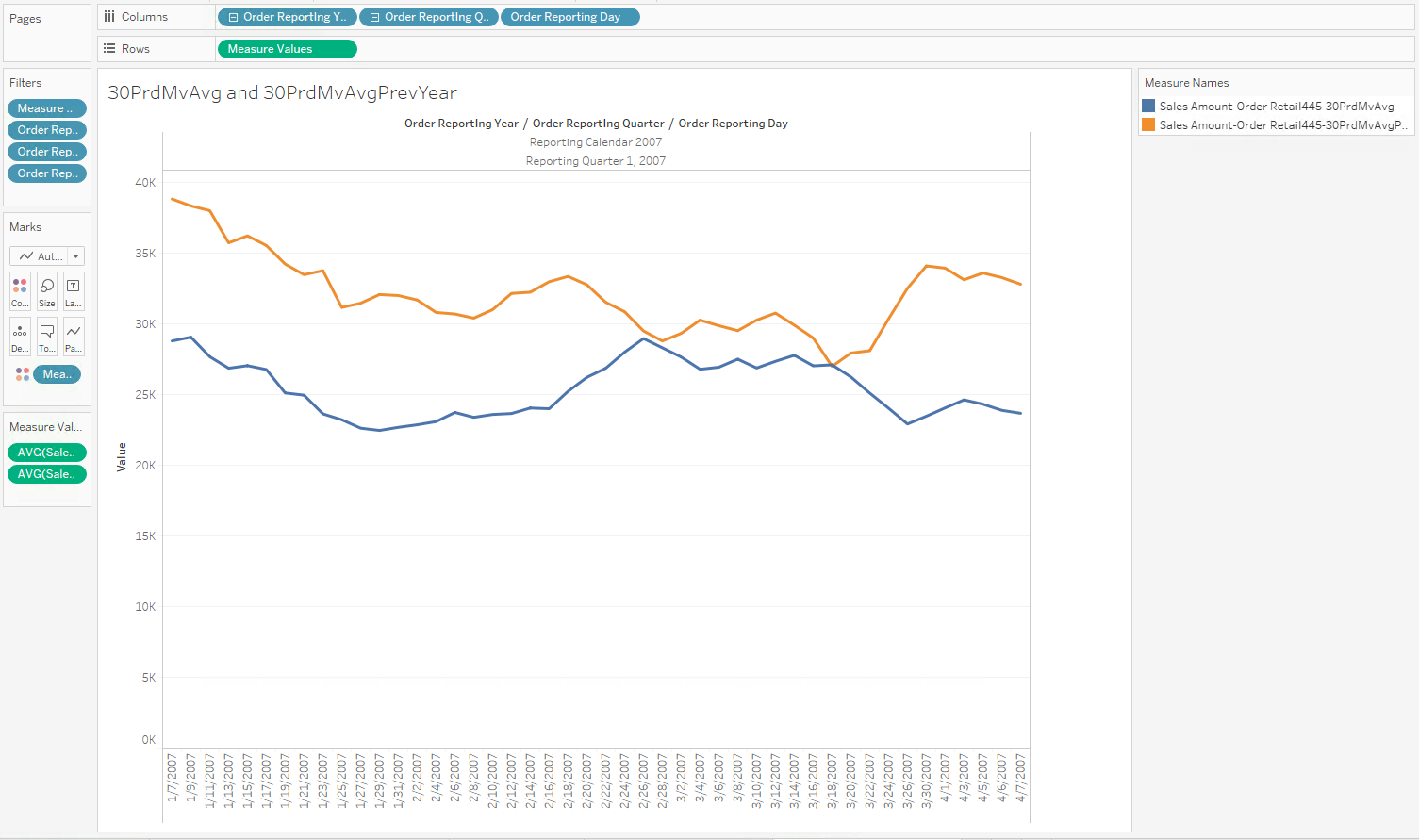
Figure 10. Excel workbook for use case 11 against 30PrdMvAvg
30-period moving average percent change compared to the previous year's
This use case compares the growth in percentage of the 30-period moving average, compared to that of the same period in the previous year.
Case 12
Calculated measure for 30-period moving average growth between years :
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvAvgPrevYearGrowthPct]
(
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvAvg]
-
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvAvgPrevYear]
)
/
[Measures].[Sales Amount-Order Retail445-30PrdMvAvgPrevYear]
Workbooks
Figure 11. Tableau workbook for use case 12
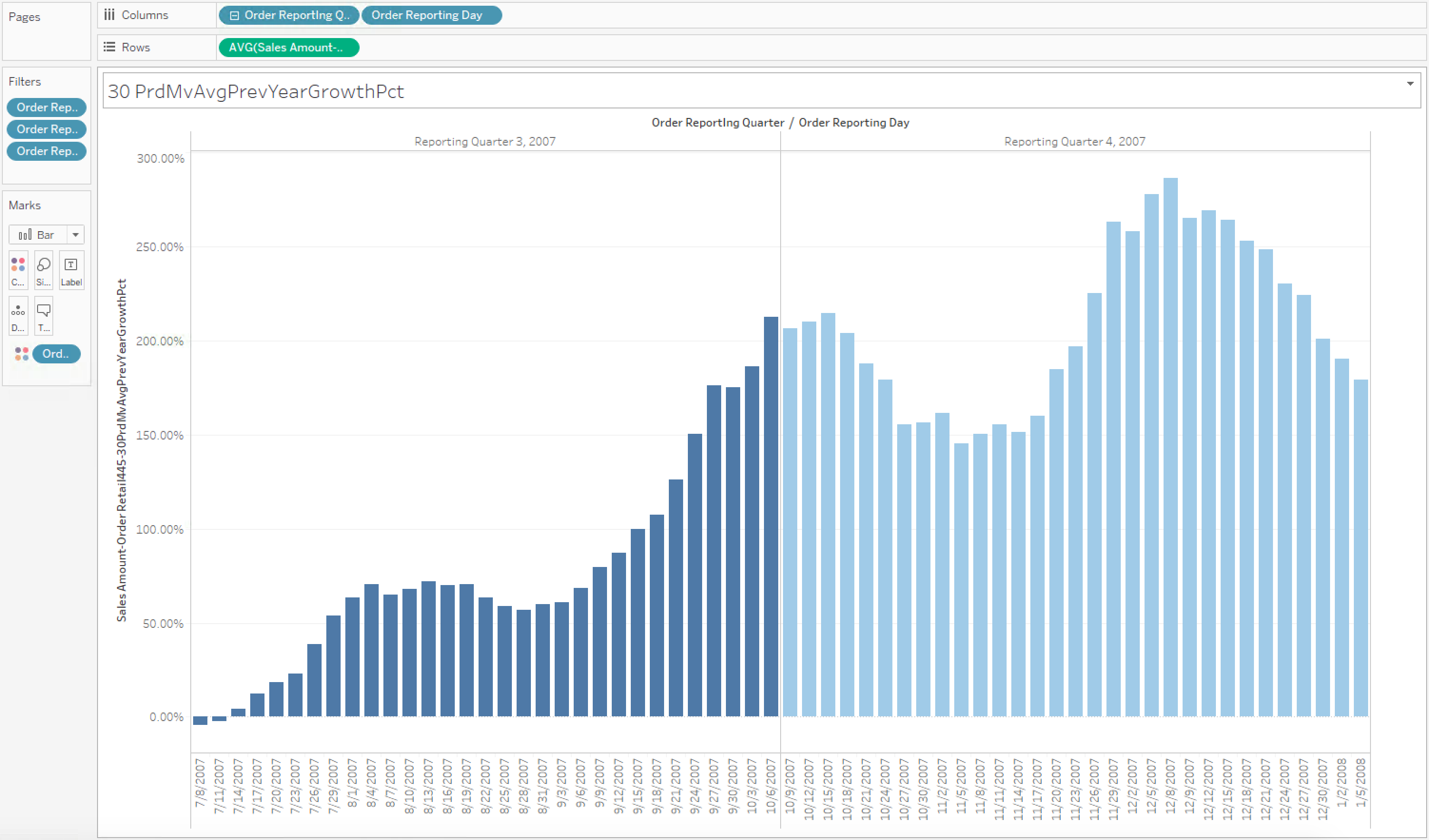
Figure 12. Excel workbook for use case 12
365-day moving window at levels higher than Day
In this use case, the calculated measure calculates a 365-day moving window at a level higher than Day.
The value of using this method to compute a moving window is that it decouples the computation from the period boundaries at higher levels. If the report user evaluates the expression at a level higher than Day (e.g. Month), the system shows the last non-empty 365-day moving window value.
This differs from other methods, such as ParallelPeriod, in that it avoids the problem of expanding the time range to the period start boundary, thereby maintaining the exact window size of 365 days up the hierarchy, even when reporting on mid-month (or higher) levels.
This scripting capability is not to be confused with the implicit "Last Non Empty" Semi-Additive aggregation measure type.
The MDX expressions used are Tail, Head, ExtractMember, and NonEmpty.
Case 13
The following expression calculates a 365-day moving average based on the last non-empty Day record for the measure [Measures].[Internet Sales Amount Local], which is a standard SUM measure.
Avg(
ExtractMember(
Tail(
NonEmpty(
Descendants(
[DateCustom].[StandardMonth].CurrentMember,
[DateCustom].[StandardMonth].[Date], SELF
),
[Measures].[Internet Sales Amount Local]
)
),
0
).Lag(364) :
ExtractMember(
Tail(
NonEmpty(
Descendants(
[DateCustom].[StandardMonth].CurrentMember,
[DateCustom].[StandardMonth].[Date], SELF
),
[Measures].[Internet Sales Amount Local]
)
),
0
),
[Measures].[Internet Sales Amount Local]
)
Filtering on subsets of children periods
Case 14
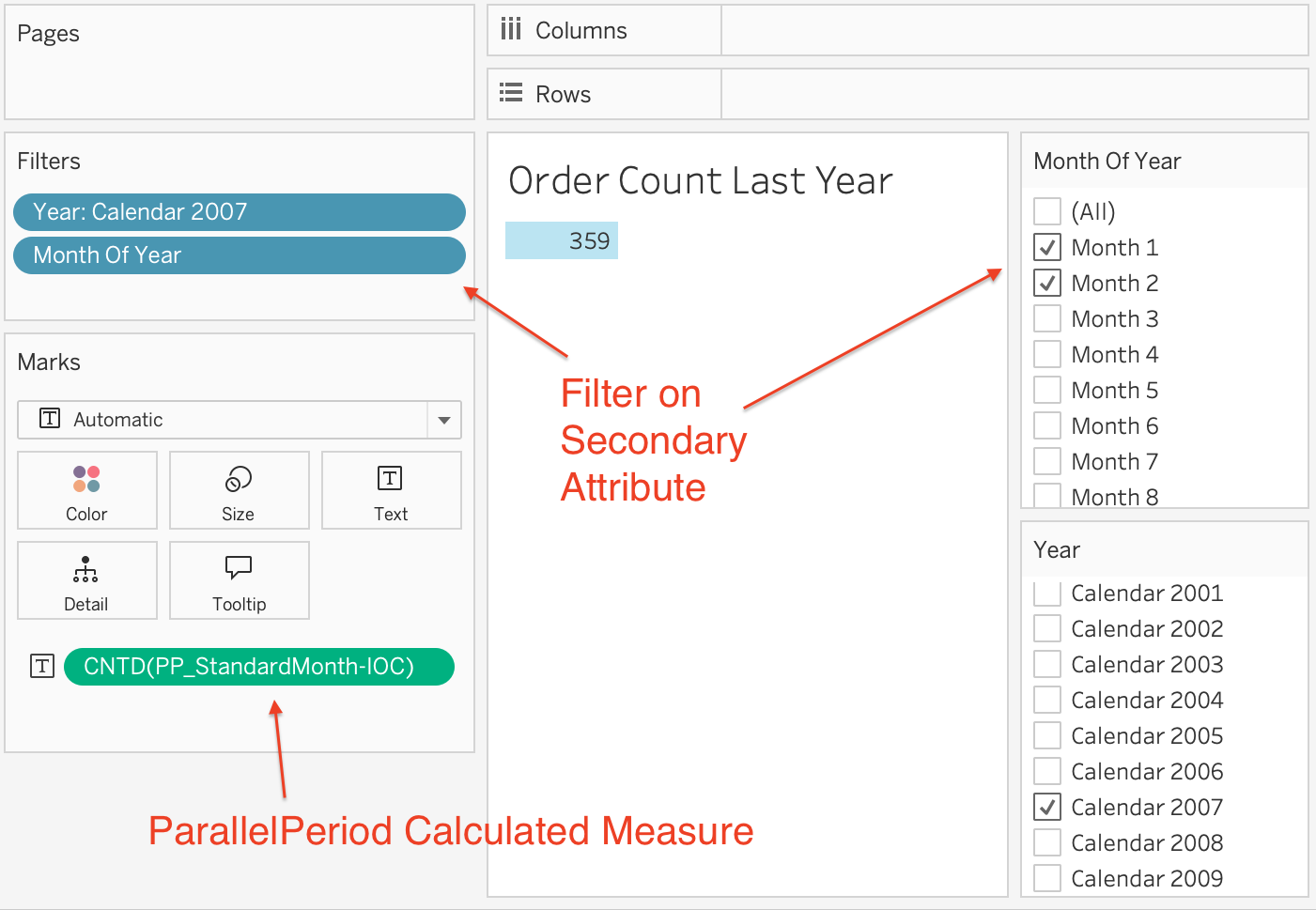
This use case selects a Last Year (i.e., ParallelPeriod) calculated measure (or similar, such as PeriodsToDate, Moving-Windows), and filters on partial child periods.
To run a query that filters on subsets of children periods (e.g. Year=2007 and Month in('January', 'March')) and requests a calculated measure that uses the "currentMember" function, the filter constraint MUST reference a secondary attribute instead of the hierarchy level. For example, to evaluate the server-side ParallelPeriod expression "PP_StandardMonth-IOC" constrained to the year 2007, and months January and February, the query must filter on the hierarchy by year "2007", and by secondary attribute "Month Of Year" values "January", "February".
Figure 13. Tableau workbook for use case 14