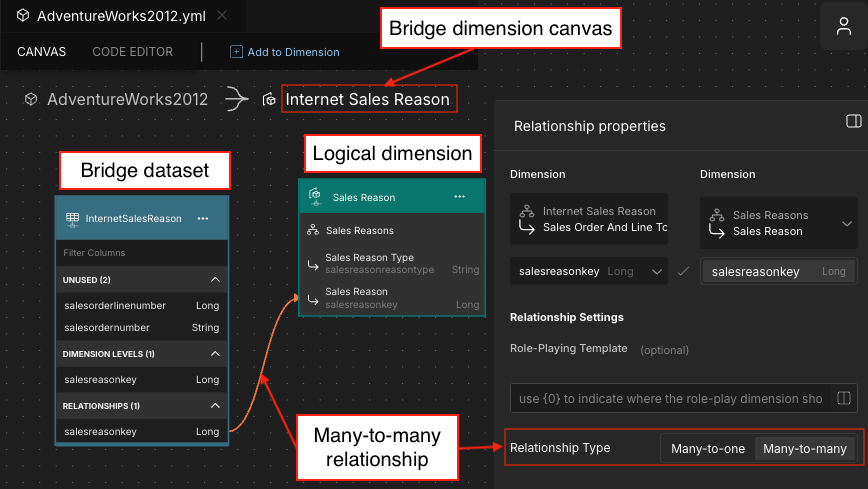
Many-to-Many Relationships
Real-world use cases do not always align with the one-to-many star schema model. Some relationships can only be represented as a many-to-many relationship. This occurs when a fact dataset row can refer to more than one row in a dimension dataset. In AtScale, this is modeled by defining a dimensional bridge to resolve the many-to-many relationship.
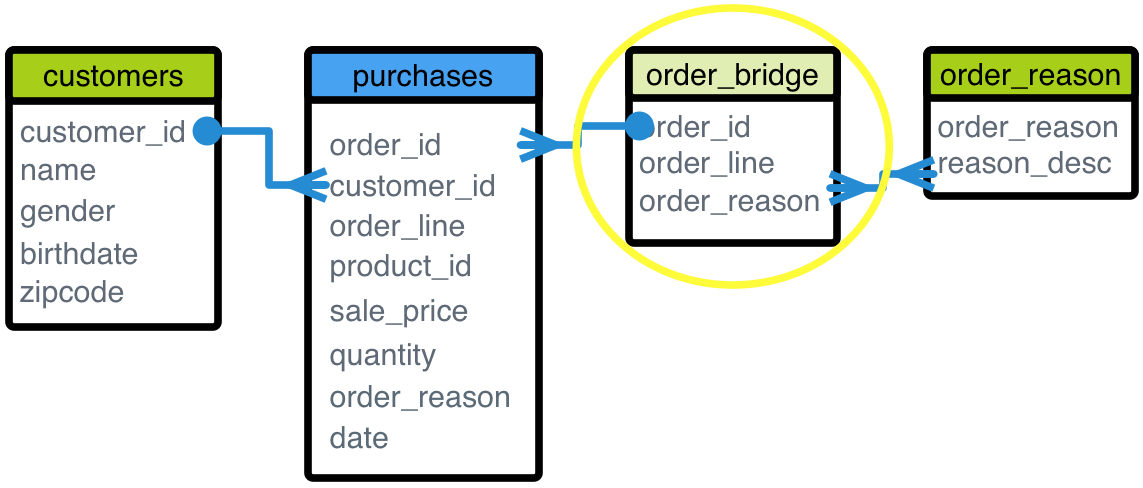
For example, a customer may have many reasons for making a purchase: While the customer-to-purchase relationship is one-to-many, the customer-to-order reason relationship is many-to-many.
To model this in AtScale, a bridge dimension is created between the fact (purchases) and the mutli-valued dimension (order reason). The bridge is considered the multi-valued dimension in this case. This is because the level used to join to the secondary dimension (order reason) is not unique. The relationship between the bridge and order reason is many-to-many.
The bridge table makes it possible to analyze attributes of the customer dimension along with the order reason. This is because the bridge table resolves the difference in granularity of the fact data. Customer information is at the granularity of an order (one customer makes an order). However, order reason is at the granularity of an order line item (a customer can have multiple line items in an order, and therefore multiple reasons for purchasing the items in an order).
Model a many-to-many relationship
You can only create many-to-many relationships on embedded dimensions.
To model a many-to-many relationship in AtScale:
-
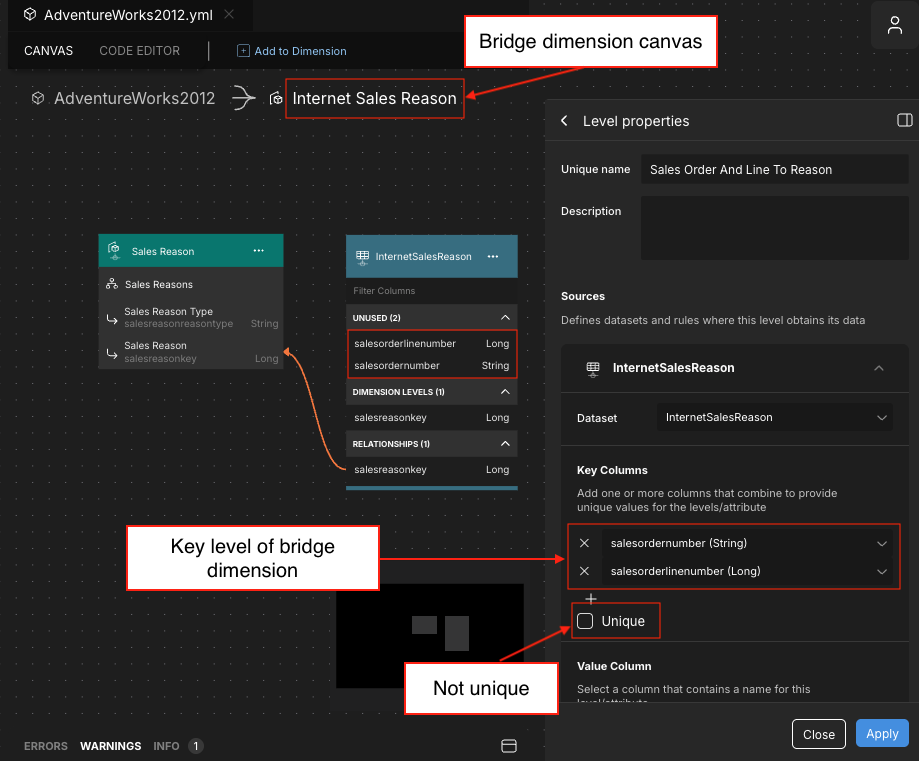
Model the bridge dimension. This must be based on its own table or view (i.e., it can't be a degenerate dimension).
-
Add the key level of the bridge dimension. Be sure to mark it as not unique by deselecting the Unique option in the Level properties panel.
-
On the Canvas for the bridge dimension, create a many-to-many relationship between the bridge dimension's dataset and the logical dimension it is joining to. Be sure to select the Many-to-many option in the Relationship Type field of the Relationship properties panel.