Using Constraint Translation for Fact Table Query Acceleration
Constraint translation is a Public Preview feature.
Constraint translation enables the AtScale engine to translate dimension filter constraints in queries to fact table partition column constraints. When the data warehouse processes the query, it can use the additional partition column constraints to accelerate it.
Overview
To enable constraint translation, you identify levels in your model as constraint translation levels, then define relationships between those levels and your fact table partition key columns. When the engine processes a query containing a filter on a hierarchy with a constraint translation level, the engine translates the filter constraints to additional fact table constraints and appends them to the end of the original query. For queries containing dimensional modifications (ParallelPeriod, PrevMember, Lag, etc.), the engine also identifies the earliest member required to satisfy the query, and applies that as a constraint.
Constraint translation behavior is triggered by inbound query filters on hierarchy levels and level aliases. It is not triggered by filters on secondary attributes.
Additionally, constraint translation is only applied to subqueries that select from dataset tables. It is not applied if the query selects from an aggregate table.
The data warehouse can then use those additional constraints to leverage its partition/cluster block pruning capabilities, enabling it to run a faster query on the fact table.
Define a constraint translation in Design Center
To add a constraint translation to a model from within Design Center:
-
Specify which dimension levels in your model are constraint translation levels:
-
In Design Center, open the dimension that contains the level you want to use as a constraint translation level. The Dimension properties panel opens.
-
In the Hierarchies section, click the context menu for the level and select Edit. The Level properties panel opens.
-
At the bottom of the panel, in the Constraint Translation Rank field, enter a rank for the level.
The rank determines the order in which the fact table constraints are appended to the outbound query. This should match the order of the physical partition/clustering configuration of the fact table.
-
Click Apply.
NoteTo configure constraint translation on a dimension imported from a read-only package, you must edit the dimension's SML. For more information, see Define a constraint translation via SML below.
-
-
Define the relationship between the constraint translation level and the partition key column in the fact table:
-
Return to the Canvas tab for the model.
-
Double-click the relationship between the fact table and the dimension that contains your constraint translation level. The Relationship properties panel opens.
-
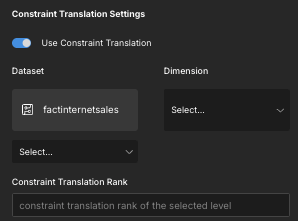
Enable the Use Constraint Translation toggle. The constraint translation settings appear.
 Note
NoteThis field is not available for relationships to degenerate dimensions.
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Dataset: Select a partition key column from the fact table.
-
Dimension: Select the constraint translation level. This must have the same data type as the partition key column.
NoteThe list only contains levels in the dimension directly connected to the fact table. You cannot select a level from an embedded dimension.
-
Constraint Translation Rank: Enter a rank for the constraint translation level. The rank determines the order in which the fact table constraints are appended to the outbound query. This should match the order of the physical partition/clustering configuration of the fact table.
If the level already has a constraint translation rank defined, this field is prepopulated with the value, and can be edited as needed. If you change the rank here, it is automatically updated for the level.
-
-
Click Apply.
-
Define a constraint translation via SML
To add a constraint translation to a model via SML:
-
Specify which dimension levels in your model are constraint translation levels. In the dimension SML file, add the
constraint_translation_rankproperty to the level attribute. For example:level_attributes:
- unique_name: Quarter
label: Quarter
dataset: DateCustom
key_columns:
- quarter
name_column: quarter_name
sort_column: quarter
time_unit: quarter
constraint_translation_rank: 1The rank determines the order in which the fact table constraints are appended to the outbound query. This should match the order of the physical partition/clustering configuration of the fact table.
-
Define the relationship between the constraint translation level and the partition key column. In the model's SML file, add the
constraint_translationproperty to the relationship connecting the dataset that contains the partition key column to the dimension that contains the constraint translation level. For example:relationships:
- unique_name: Internet_Sales_Date_Custom
from:
dataset: Internet Sales
join_columns:
- orderdatekey
to:
dimension: Date Custom
level: Date
constraint_translation:
level: Quarter <--- This references the level in the "relationships/unique_name/to/dimension" that has the "constraint_translation_rank" property.
from_columns:
- part_year_quarter <-- This references a column in the "relationships/unique_name/from/dataset" that is partitioned or clustered.
For more information on the constraint_translation_rank and constraint_translation properties, see Dimension and Model in the AtScale SML Object Documentation on GitHub.